lv obstroction flow | ventricular outflow tract obstruction diagnosis lv obstroction flow Left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction is a condition that restricts blood flow from the left ventricle of the heart. LVOT obstruction is defined as a peak gradient of at . Directions. Save to My Recipes. Step 1 In a blender, blend ice cream, milk, and malted milk powder until smooth. Add more milk and continue to blend to desired consistency, if needed. Step 2.
0 · ventricular outflow tract obstruction symptoms
1 · ventricular outflow tract obstruction diagnosis
2 · ventricular outflow tract obstruction causes
3 · lvot gradient chart
4 · left ventricular outlet obstruction
5 · left ventricular outflow obstruction symptoms
6 · left ventricular outflow obstruction management
7 · left ventricular outflow obstruction causes
The historic acadian Village of Nova Scotia is located on a beautiful 17 acre site. See the amazing views of the breathtaking Pubnico harbour,which is dotted with picturesque islands, when you explore our nature trail. The community of Pubnico is recognized as the oldest region still Acadian.
Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) is commonly associated with systolic anterior motion (SAM) of the mitral valve. Congenital heart disease is an important cause in the paediatric population.
Left ventricular outflow tract obstructions (LVOTOs) encompass a series of stenotic lesions starting in the anatomic left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) and stretching to . Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a genetically determined disease that commonly results in obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT), which can produce .Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction is a cardiac condition characterized by an obstruction to blood flow from the left ventricle. Timely diagnosis, appropriate management, and .
Left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction is a condition that restricts blood flow from the left ventricle of the heart. LVOT obstruction is defined as a peak gradient of at . Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) limits blood flow from the left ventricle. The level of obstruction can be valvular, sub-valvular, or supravalvular. It can include .The surgical management of patients with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy can be extremely challenging. Relieving the left ventricular outflow tract obstruction in these patients . Ventricular U‐turn looping in susceptible individuals causes a crucial overlap of the inflow and outflow portions of the left ventricle (LV), resulting in SAM, LVOT obstruction, and .
Answer: Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction (LVOTO) 1-17. Underlying Principles. . Venturi effect causes the mitral valve to lift anteriorly towards increased velocity of blood flow 2. Causes physical obstruction of outflow 3; SAM of the MV additionally generates mitral regurgitation, . Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a genetically determined disease that commonly results in obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT), which can produce chest discomfort, dyspnea, fatigue, and syncope. . • Increase afterload – Pressors can be used to increase afterload, which decreases the velocity of flow in the LVOT . Severe aortic stenosis (AS) commonly leads to progressive left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy in response to chronic pressure overload. LV volumes are also noted to decline with increasing age.1 Due to combined effects of concentric LV hypertrophy and lower LV volumes, intraventricular pressure gradients may develop, leading to various degrees of LV obstruction .
Though left ventricular outflow tract obstruction is usually a dynamic phenomenon which could happen to any ICU patient, this chapter has been thrown into the Cardiothoracic ICU section mainly because of completely irrational personal reasons, i.e. that's the sort of place where the author encounters it most frequently, usually in patients waiting for or recovering .Left Ventricular Outflow Obstruction. Subaortic Stenosis, Bicuspid Aortic Valve, Supravalvar Aortic Stenosis, and Coarctation of the Aorta. Jamil Aboulhosn; and ; John S. Child; . valvar, or supravalvar. These obstructions to forward flow may present alone or in concert, as in the frequent association of a bicuspid aortic valve with . Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) accounts for 5–10% of all congenital heart defects. LVOTO occurs at the valvar (70%), subvalvar (14%), and supravalvar (8%) level, and several levels of obstruction often coexist (8%) [].Another type of muscular subaortic stenosis, present with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, is known as hypertrophic . This may particularly provide efficiency during periods of high heart rate or threat. The loop's principle liability is its vulnerability to genetic and acquired anatomic perturbations, rendering it vulnerable to LV outflow obstruction because of an overlap between LV ejection flow and the mitral valve.
There was a significant difference in 2D derived left ventricular end‐diastolic cavity M‐mode dimension (37 vs 33 mm [P = .02]) and left ventricular end‐systolic cavity M‐mode dimension (23 vs 21 mm [P = .03]), indicating the left ventricular cavity size was smaller in the patients with ICG of 36 mm Hg or higher. FIGURE 4.
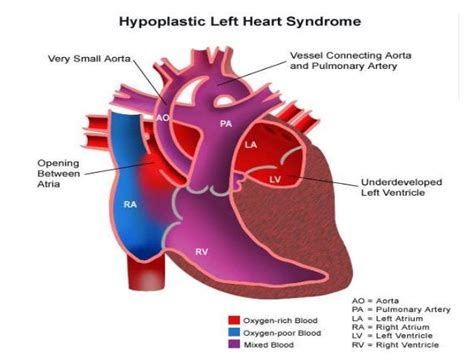
Obstruction in the Newborn • Ductus dependent for systemic blood flow • Oxygenation typically good –may not look cyanotic but depends on having adequate L-R flow across the atrial septum • Babies may look remarkably well at birth, with ductal closure present with symptoms of poor perfusion – lethargy, poor feeding, appearing The left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) (also sometimes called the aortic vestibule) is considered to represent the region of the left ventricle that lies between the anterior cusp of the mitral valve and the ventricular septum. It directs blood towards the aortic annulus and through the aortic valve during systole. In the 1980s and 1990s, the evolution of 2-dimensional echocardiography and Doppler echocardiography provided an alternative noninvasive approach for the assessment of both cardiac anatomy and hemodynamics in patients with structural heart disease. 2 By measuring blood flow velocities noninvasively, Doppler echocardiography was able to provide .
ventricular outflow tract obstruction symptoms
Left Ventricular Outflow Obstruction: Subaortic Stenosis, Bicuspid Aortic Valve, Supravalvar Aortic Stenosis, . Obstruction may be subvalvar, valvar, or supravalvar. These obstructions to forward flow may present alone or in concert, as in the frequent association of a bicuspid aortic valve with coarctation of the aorta. All of these lesions .regurgitation and left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (turbulent flow). (C) Estimated intraventricular gradient of 40 mm Hg with a peak velocity across the left ventricular outflow tract of 3.2 m/s. (D) Immediately after intravenous beta-blocker treatment: a significant reduction in mitral valve regurgitation, in combination with (E) a .
a Preoperative transthoracic echocardiography (parasternal long axis view) showing left ventricular hypertrophy, asymmetric septal hypertrophy, and SAM of the mitral valve.b Color Doppler showing a mosaic blood flow signal pattern in the LVOT.c Continuous wave Doppler showing a backward shift of the peak LVOT flow.d Transesophageal echocardiography with .
Severe left ventricular hypertrophy: Left ventricular hypertrophy refers to the thickening of the muscular wall of the left ventricle. If the hypertrophy is severe, it can cause obstruction to blood flow from the left ventricle to the .of flow in the LVOT and reduction of lateral pressure, tri-ggering a venturi effect that “attracts” the anterior valve of . Obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOTO) caused by SAM is found in one-third of patients with HCM at rest (13, 15) and occurs in up to two thirds of symptomatic pa- . Left ventricular outflow obstruction comprises cardiac lesions that obstruct blood flow from the left ventricle to the systemic circulation. The obstruction may occur at three levels: (1) valvar or near the valvar level (valvar, subvalvar and supravalvar aortic stenosis), (2) arterial level (coarctation of the aorta, interrupted aortic arch, midaortic syndrome), and (3) the .
A left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) may be due to a defect in the aortic valve, or a defect located at the subvalvar or . A ventricular outflow tract obstruction means there is a limitation in the blood flow out of either the right or left ventricles of the heart, depending on where the obstruction is. This can lead .The diagnostic features of left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) were characterized >50 years ago.1-3 In contrast, the features of mid-cavitary obstruction (MCO) at cardiac catheterization remain poorly understood and limited to case reports.4-6 Accordingly, we describe the invasive hemodynamic findings in MCO using a .Outflow graft obstruction in left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) is a rare complication whose cl. . Left ventricular assist device flow was 5.6 L/min, the pulsatility index was >8. The patient was on oral anticoagulation [target international normalized ratio (INR) 2.5–3.0]. The patient underwent PA and two stents were implanted (Aortic .
Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction—be prepared! . the understanding of normal left ventricular flow patterns24-28. MRI shows the normal direction of systolic flow to be slightly curved to the right as the axis of the aorta is at a slight angle to the ventricle27. Contrast echocardiography has alsoLeft Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction. The main pumping chamber of the heart, the left ventricle, is a muscular structure that contracts down from holding around 90ml of blood when relaxed to 30ml of blood when fully ejected. . In some circumstances, this can enlarge or “hypertrophy” and restrict the flow of blood out of the heart . Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) accounts for 3.5–10% of all congenital heart defects [1, 2], with the majority of patients being male.LVOTO occurs at the valvar (70%), subvalvar (14%), and supravalvar (8%) levels, and several levels of obstruction often coexist (8%) [].LVOTO may be further compounded by other left-sided anomalies (small . Figures illustrating the pathophysiology and management of left ventricular outflow-tract obstruction. Figure (A) illustrates the pathophysiology and figure (B) illustrates management. . Labovitz AJ. Systolic and diastolic flow abnormalities in elderly patients with hypertensive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988;12:989 .
However, CT also allows the quantification of severity by planimetric measurements of left ventricular obstruction. . (gradient may be <50 mmHg due to low flow) or AR is severe and LV end-systolic diameter >50 mm and/or ejection fraction <50 %, mean Doppler gradient is ≥50 mmHg and marked LV hypertrophy, or mean Doppler gradient is ≥50 .
ventricular outflow tract obstruction diagnosis
dolce gabbana dress wedding
The flow generated by the obstruction was directed toward the LV apex and appeared from late systole to early diastole. The obstructio . We report the case of an 88-year-old man who developed a mid-left-ventricular (LV) obstruction caused by apical pacing to manage third-degree atrioventricular block. The flow generated by the obstruction was .
Adolescent Cardiac Issues. Jennifer M. Blake MD, in Pediatric Clinics of North America, 2014 Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction. Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (aortic valve, subaortic area, or supra-aortic area) and coarctation of the aorta may have complaints of chest pain, but will usually also have other symptoms, such as dizziness, fatigue, and/or syncope .
dolce gabbana escape to panarea 100 ml

ventricular outflow tract obstruction causes
Traversez 200 ans d’histoire et devenez le témoin privilégié de la naissance de l’Acadie du Nouveau-Brunswick! Le Village historique acadien est un complexe touristique composé d’un sentier parcourant 2.2 km, bordé d’une quarantaine de bâtiments historiques tous animés par des interprètes costumés et bilingues (anglais et .
lv obstroction flow|ventricular outflow tract obstruction diagnosis